Aims
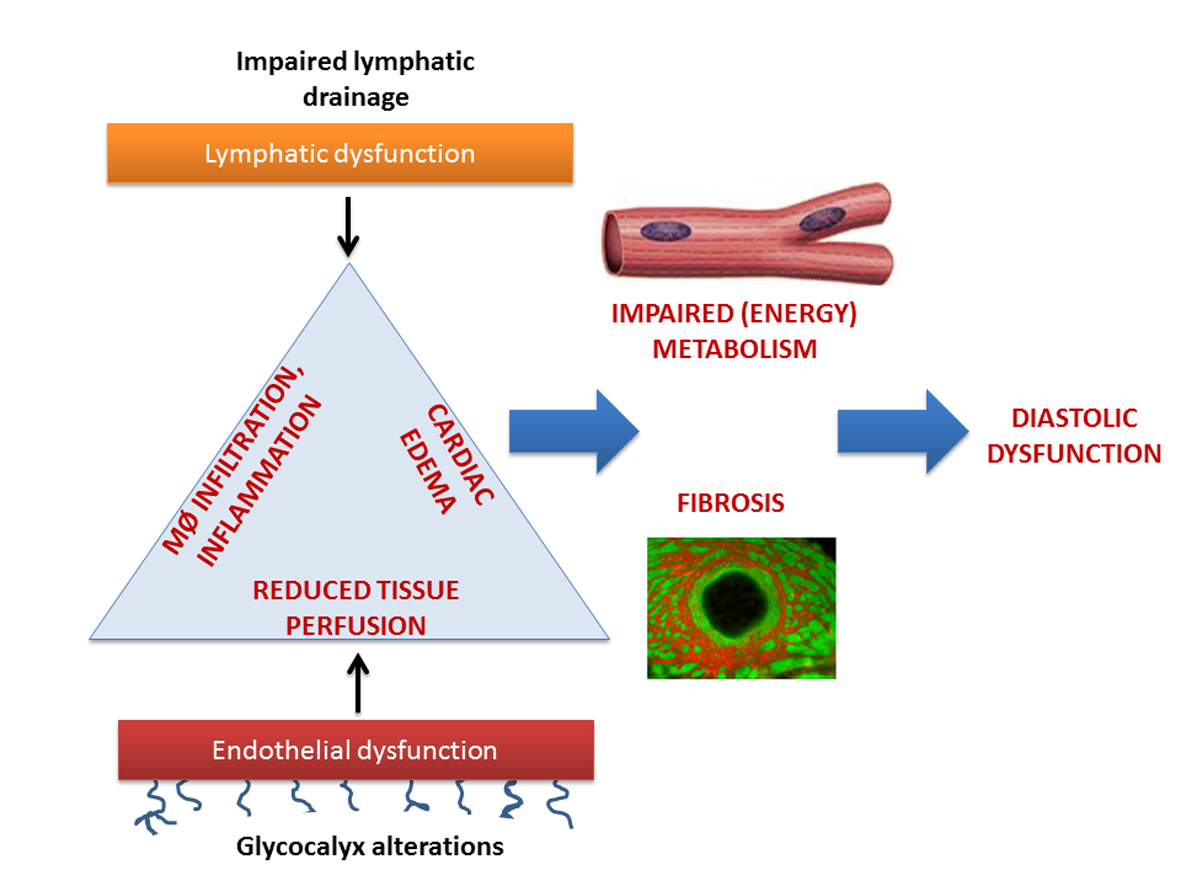
The key aims of LYMIT-DIS are to determine the molecular and cellular mediators, including gender-specific disease mechanisms, involved in:
- Cardiac microvascular remodeling and dysfunction and vascular hyperpermeability vs. cardiac inflammation and edema
- Cardiac microvascular perfusion disturbances, vascular remodeling / angiogenesis vs. cardiac metabolic dysfunction
- Cardiac lymphangiogenesis & lymphatic transport dysfunction vs. inflammation and edema
- Regulation of myocardial fibrosis vs. cardiac inflammation, ischemia, and hypertrophy
The ultimate goal of LYMIT-DIS is to increase our understanding of the mechanisms involved in the cardiac diastolic dysfunction in HFpEF, with the aim to identify and evaluate innovative treatments to limit the cardiac impact of metabolic syndrome and to prevent the transition from cardiac dysfunction to Heart Failure.